Allergy is an increasingly common condition where one’s immune system is oversensitive to certain agents. These agents, called allergens, can be something we ingest or come into contact with in our surrounding envionment
The immune system helps our body fight off germs such as virus and bacteria. However, sometimes, for reasons still unclear, the immune system may misinterpret certain harmless agent (allergens) as something foreign and dangerous. Allergy is due to the immune system being triggered to set off a cascade of reactions.
In Hong Kong some of the major allergens reported include:
· Eggs
· Nuts (peanuts, walnuts, hazelnuts, macadamian nuts)
· Soybean
· Wheat
· Fish
· Crustaceans/ shellfish
· Milk
· House dust mites
· Animal dander
· Pollen (tree, grass, weed)
· Mould
· Drugs ( antibiotics, analgesics)
· Latex
What symptoms can allergies cause?
Allergies can affect many different parts of our bodies and result in a wide range of symptoms:
| Affected areas | Common symptoms |
| Eyes (Allergic conjunctivitis) | Red, itchy, watery, burning, swollen eyes; dark circle under the eyes (allergic shiners) |
| Nose (Hay fever/ Allergic rhinitis) | Itchy, runny, stuffy nose; sneezing; postnasal drip; recurrent sinus infection; chronic mouth breathing |
| Ears | Fluid in the ear recurrent middle ear infection |
| Lungs(Asthma) | Coughing; wheezing; chest tightness; difficulty breathing |
| Skin/ Mouth(Atopic eczema/ Urticaria) | Itchy dry skin; itchy welts or hives; swelling of face and lips; tingling sensation in the mouth |
| Stomach(Food allergy) | Vomiting, diarrhoea, stomach cramps |
Anaphylaxis
This is the name given to a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction. They usually come on very quickly after you have been exposed to something you are severely allergic to. You may have swelling, itching or a rash. Some people may have trouble breathing and a tight feeling in their chest. Other people may have stomach cramps, nausea or diarrhoea, feel dizzy and even become unconscious. Anaphylaxis is potentially life threatening and requires urgent medical treatment.
Call 999 if you or your child
· Suddenly develops swollen lips, mouth, tongue or throat.
· Your throat feels swollen or struggles with swallowing.
· Your breathing becomes very rapid or you struggle to catch your breath.
· Your skin, lip or tongue becomes pale, blue or grey.
· You suddenly feels dizzy, faint or very confused.
· Your child goes limp, floppy or not responding to you like they normally would.
Who is at risk of developing Allergic Disorders?
Studies shows that allergies have a strong hereditary link. Therefore, your child will have a greater tendency to develop an allergy if you, your partner, or one of your children has a history of allergic disease.
By making the diagnosis and identifying the triggers early, your doctor can develop the best therapeutic approach to potentially modify the course of the disease progression and prevent subsequent development of other related conditions such as asthma.
Do I Have an allergy?
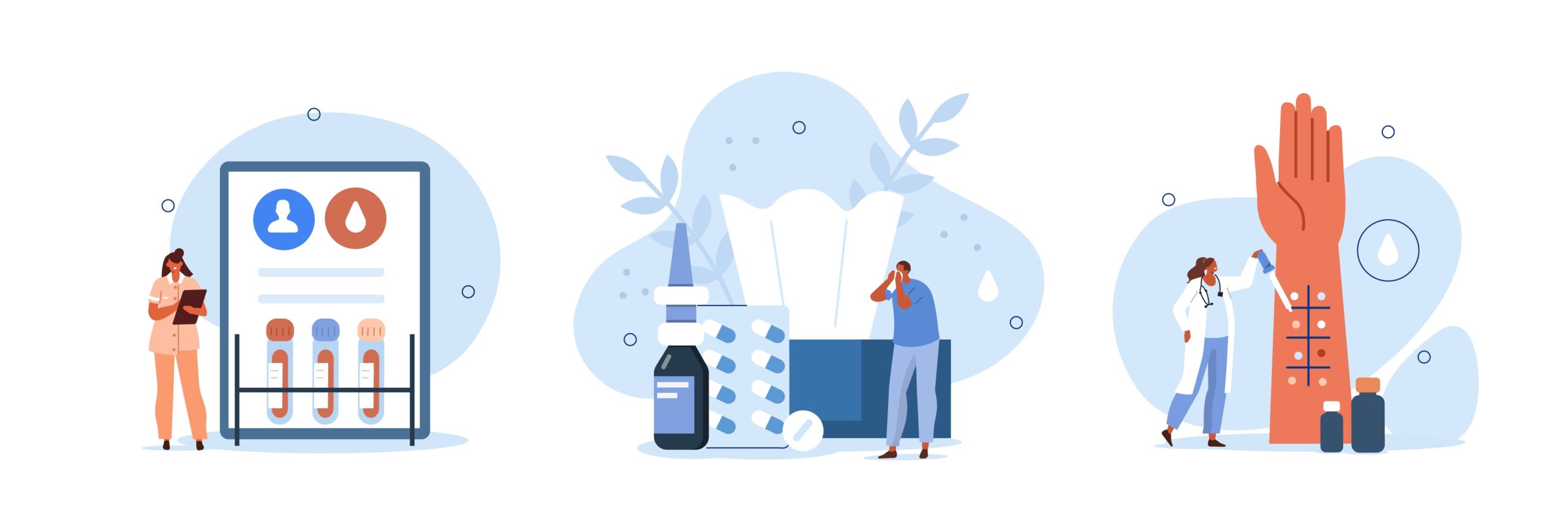
If you suspect you or your child may have an allergy, please book an appointment with one of our GPs to discuss the next steps. Diagnosis begins with a careful evaluation of the patient’s clinical history and a physical examination. Specific allergy tests may be performed to identify specific allergens.
Tests that may be helpful for diagnosis include:
· Skin-prick test– small amount of allergen is injected into the skin to see if it forms a wheel.
The selection of allergens tested will depend on your age and clinical history
Results are usually available within 20 minutes
· Patch test– allergens are applied to the skin for a period (usually you go home with a big plaster over your back and returns to clinic a few days after) to see if it develops a skin reaction/redness or wheel. This type of testing is usually done for suspected skin allergies. Results are usually available within a few days.
· IgE blood test eg. IgE ALEX allergy test- this test involves collecting a small amount of blood to check for antibodies to allergens as well as components making up the allergen. This helps to determine the severity of the allergic reaction one may have. The blood will be sent to a medical laboratory and the results are usually available within 1-2 weeks.
Please note that all tests should always be discussed with a medical professional who knows your clinical symptoms and medical history.
Food Intolerance vs food allergens
Many people use the term food intolerance interchangeably with food allergy. However, the two conditions are very different. Food intolerances are due to the digestive system finding it difficult to break down certain foods causing symptoms of bloating, tummy cramps and/or diarrhoea. An example of this is lactose, a sugar found in milk.
If you are unsure if you have a food intolerance or food allergy you should book an appointment with a GP to discuss your symptoms.
Treatment
The best way to manage an allergy is to eliminate the culprit from your environment. Medication such as antihistamines and steroids are also useful to manage established allergic reactions.
However sometimes allergens are very difficult to completely eradicate and symptomatically hard to control. Over the past decade immunologists have also developed ways to remove the root cause of an allergy- a therapy called Allergy immunisation or allergy desensitisation.
Small particles of the allergen (allergy shots) are administered to trigger a small but reactive immune response. The idea is that your immune system will recognise it and build up an immune tolerance. With repeated treatments the immune response will gradually diminish and so will the clinical symptoms.